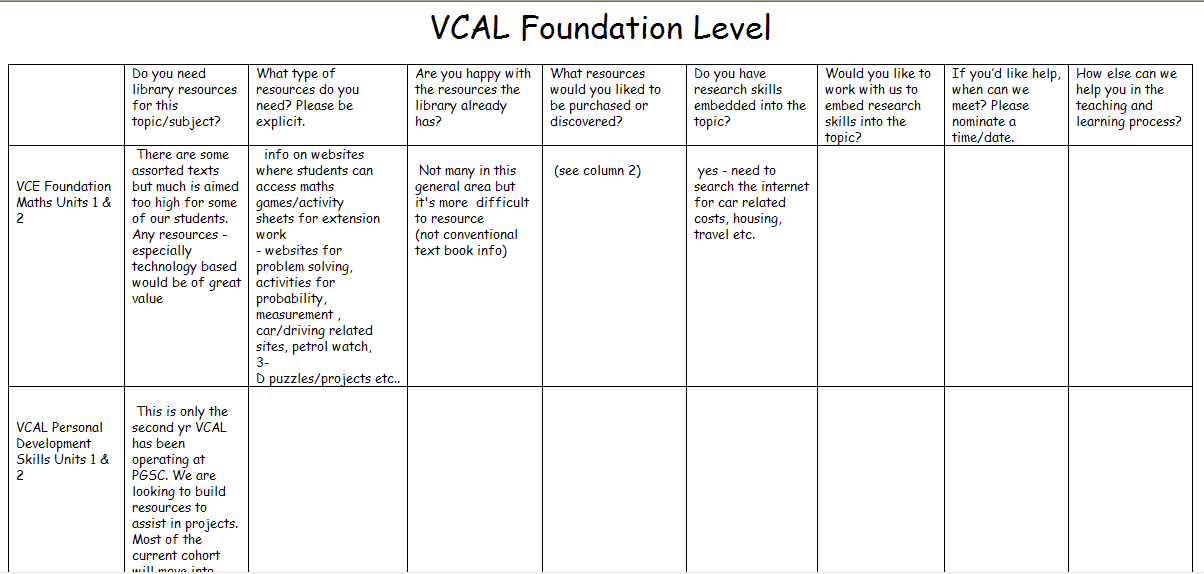
On their arrival at Preston Girls’ Secondary College earlier this year, teacher librarians Judith Way and Reina Phung grappled to get a handle on the curriculum requirements of the college. Job-sharing the 1.0 position, with no support staff, Judith and Reina found it difficult to find the time to meet with subject coordinators to ask for their input. Aware of the few audio visual resources and a collection that needed updating, they decided to set up a ‘Curriculum Audit’ wiki.
It was decided that the wiki was to be kept private, for the use and eyes of the school staff only. Staff were emailed an introduction and request to contribute to the wiki. The email contained a word document attachment that included detailed instructions and screenshots on how to contribute to the wiki. Staff were then asked to contribute their thoughts on a number of questions:
- Do you need library resources for this topic/subject?
- What type of resources do you need? Please be explicit.
- Are you happy with the resources the library already has?
- What resources would you liked to be purchased or discovered?
- Do you have research skills embedded into the topic?
- Would you like to work with us to embed research skills into the topic?
- If you’d like help, when can we meet? Please nominate a time/date.
- How else can we help you in the teaching and learning process?
Some staff not only responded quickly and in some detail, but were enthused about the possibilities of wikis. One teacher, Les Kyle, proceeded to quickly create her own extremely detailed wiki for her VCAL class; the whole curriculum, topics and links to resources (with some contributions from Judith and Reina). This wiki was kept private within Preston Girls’ (using an email to the students’ email address inviting them to join the wiki) as full student names appeared on the wiki and discussions between teacher and students took place. Judith and Reina were proud to think that their Curriculum Audit wiki was the catalyst for Les’s fabulous wiki.
However, many staff did not know what a wiki was, and some had trouble even logging on. The ideal situation would have been an introductory session during a Curriculum Day for those interested/needing guidance. However as all Curriculum Days had been allocated to specific topics (Literacy), Judith and Reina continued to work one-to-one with interested teachers. Judith and Reina believe that something like the SLAV Web 2.0 course for teachers would be terrific, as they often felt that the majority of the teaching staff would benefit from the introduction to the Web 2.0 tools out there that can enhance teaching and learning.
The idea that wikis were the ideal tool for student/student and student/teacher (and teacher/teacher) collaboration was introduced to teachers. That students projects could be completed in teams, and the teacher automatically alerted by email to when contributions had been added. Students taking full responsibility for their own learning becomes apparent when those with access to the wiki can see (and also have email alerts) who has contributed what to the wiki. The way discussions and comments are structured means that students have to think about their responses, rather than perhaps plagiarise by cutting and pasting.
The bonus was that discussions about wikis and blogs now regularly take place and teachers who have not yet made a contribution to the wiki promise to do so when the VCE classes finish. The new ICT Coordinator has begun his own blog. And the teachers who contributed to the wiki will have the best resourced subjects in the school!
The only problem that Judith and Reina found was that the initial wiki grew so large that it had to be split into two; years 7-10 and years 11-12.